
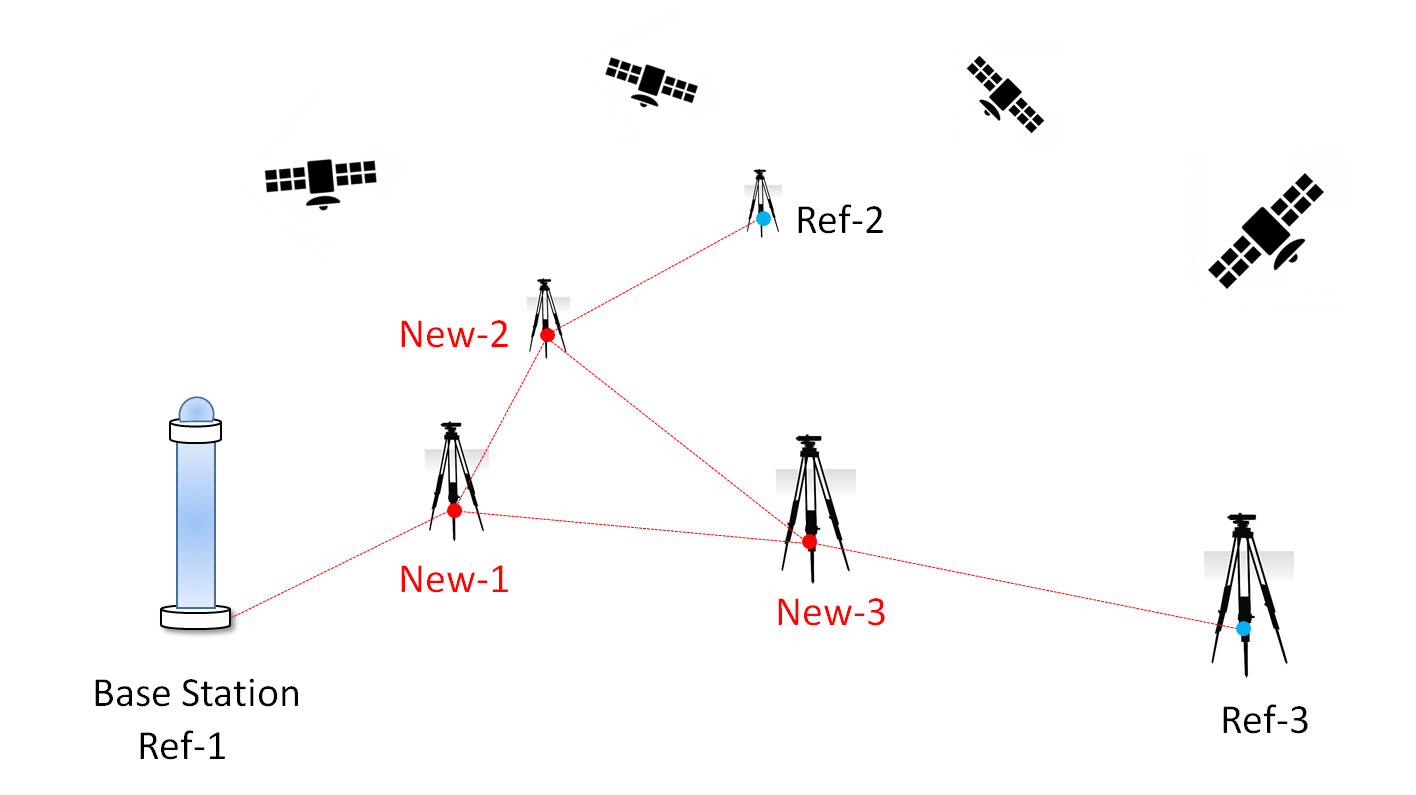
Static GPS surveying is a relative positioning technique which employs two (or more) stationary receivers simultaneously tracking the same satellites. One receiver, the base receiver, is set up over a point with precisely known coordinates such as a survey monument. The other receiver, the remote receiver, is set up over a point whose coordinates are unknown. This method of surveying is based on collecting simultaneous measurements at both the base and remote receivers for a certain period of time, which, after processing, yield the coordinates of the unknown point. This type of survey is primarily used to create control where no control exists to very high accuracies.
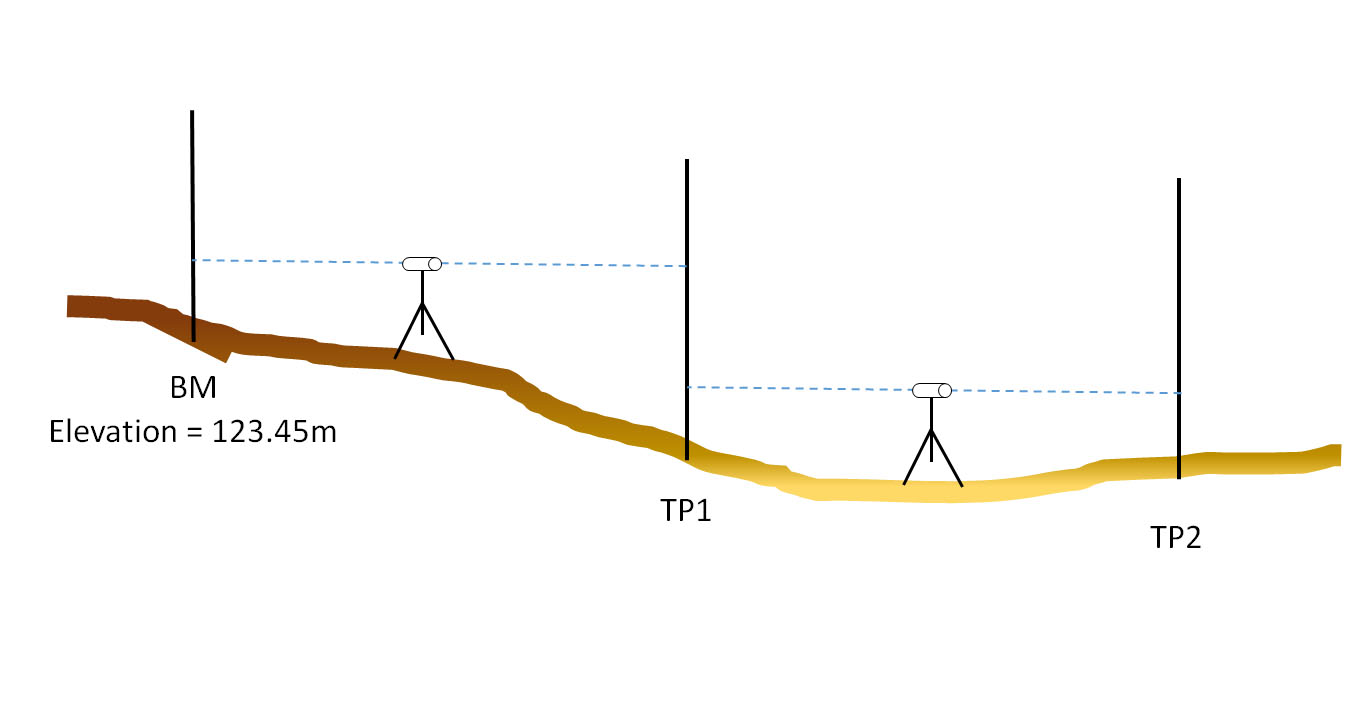
Levelling is the most widely used method of obtaining the elevations of ground points relative to a reference datum and is usually carried out as a separate procedure to those used in fixing planimetric position. The basic concept of leveling involves the measurement of vertical distance relative to a horizontal line of sight. Hence it requires a graduated staff for the vertical measurements & an instrument that provides a horizontal line of sight.
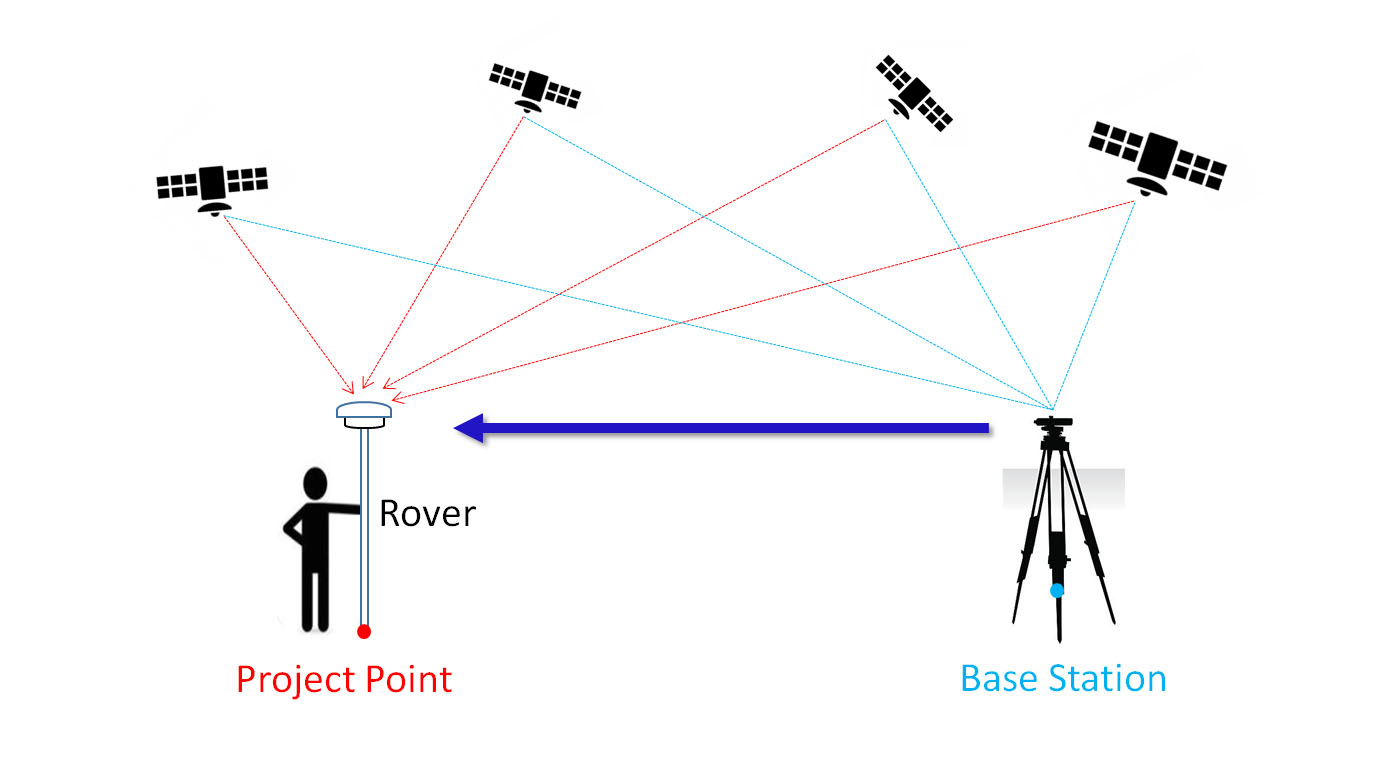
RTK surveying is a relative positioning technique which measures positions using two GPS(GNSS) antennas in real time. One is setup on a static point with fixed coordinates and is known as the base station. It uses a high frequency radio to transmit its raw observations to the second unit (known as the rover) and then the rover uses both observations to compute a position relative to the base location in real-time. RTK surveying requires reliable communication between base and rover units and works best with short baselines as the precision of RTK measurements decreases as the baseline length increases.
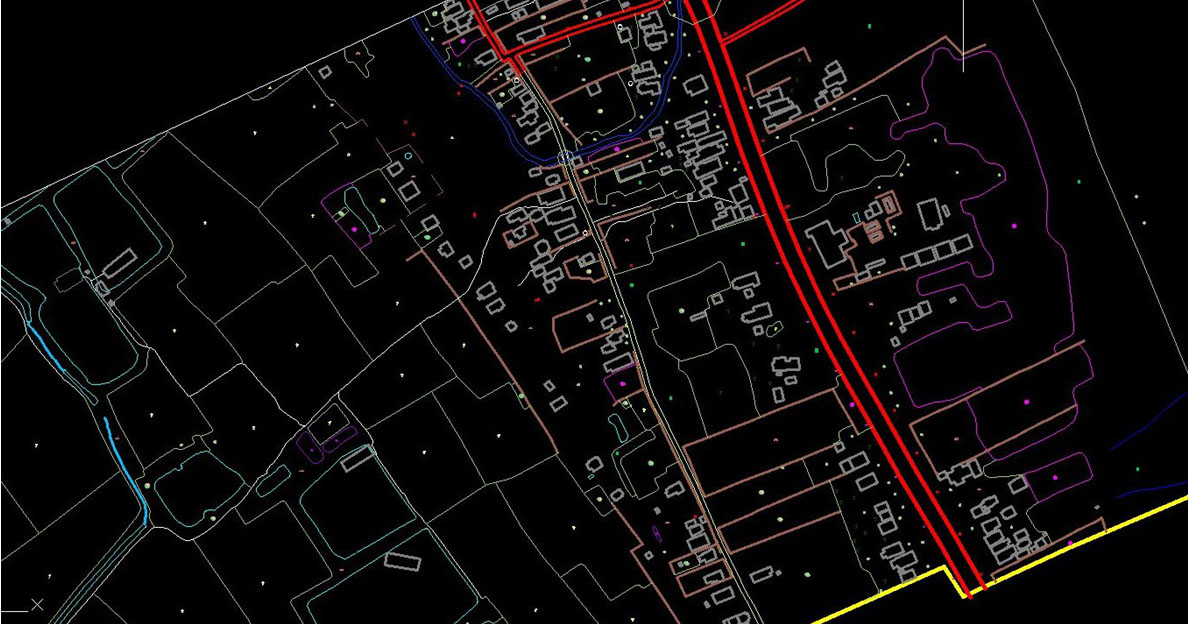
Maps are key to representing the features and layout of the world, from the local to the global. Satellite images are used to create wide-area topographic maps. And, hybrid data from ground surveys and UAV cameras are used to create detailed topographic maps.
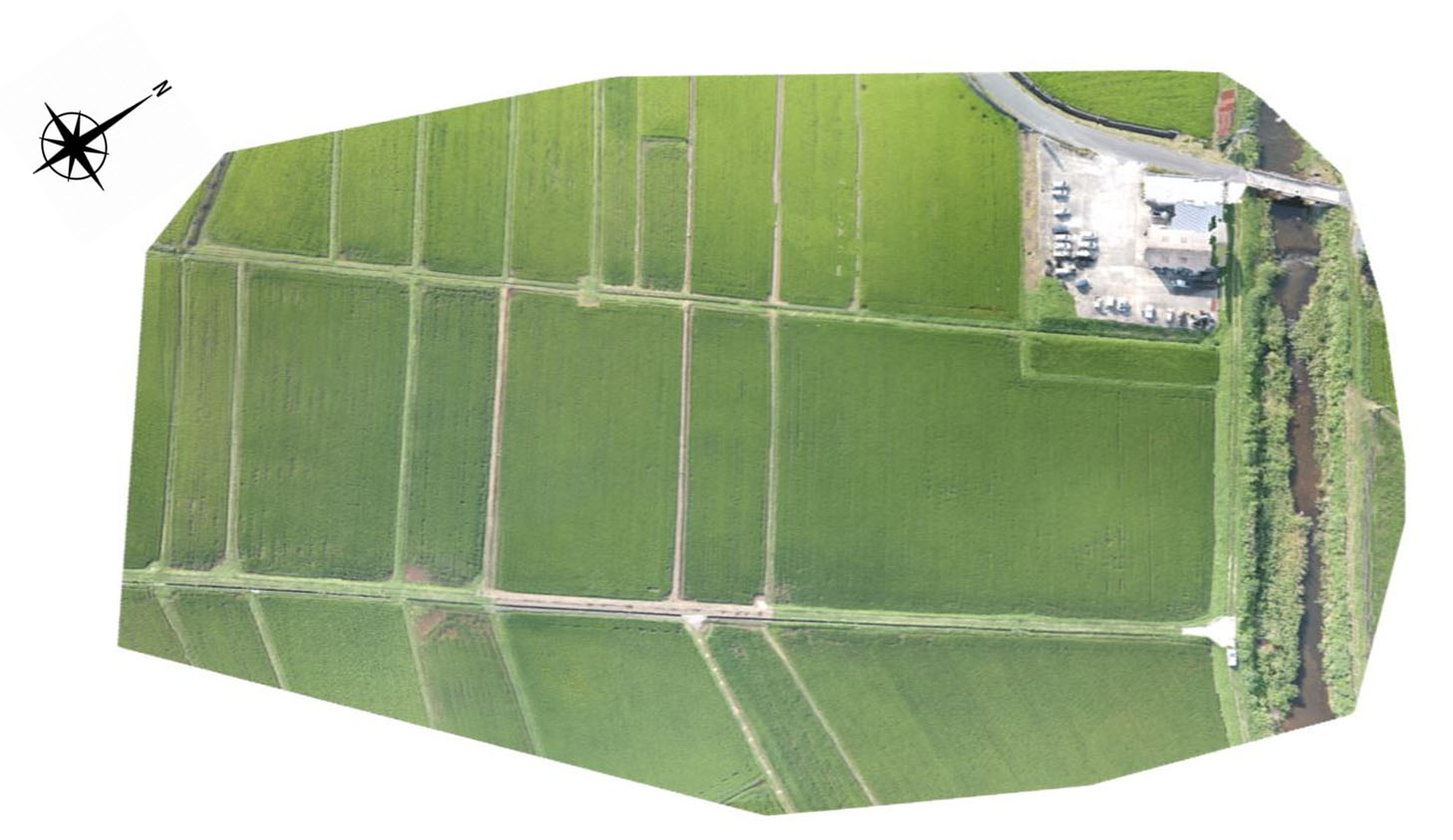
An orthophoto or orthomosaic is an aerial photograph geometrically corrected ("orthorectified") such that the scale is uniform: the photo has the same lack of distortion as a map. Unlike an uncorrected aerial photograph, an orthophotograph can be used to measure true distances, because it is an accurate representation of the Earth's surface, having been adjusted for topographic relief, lens distortion, and camera tilt.

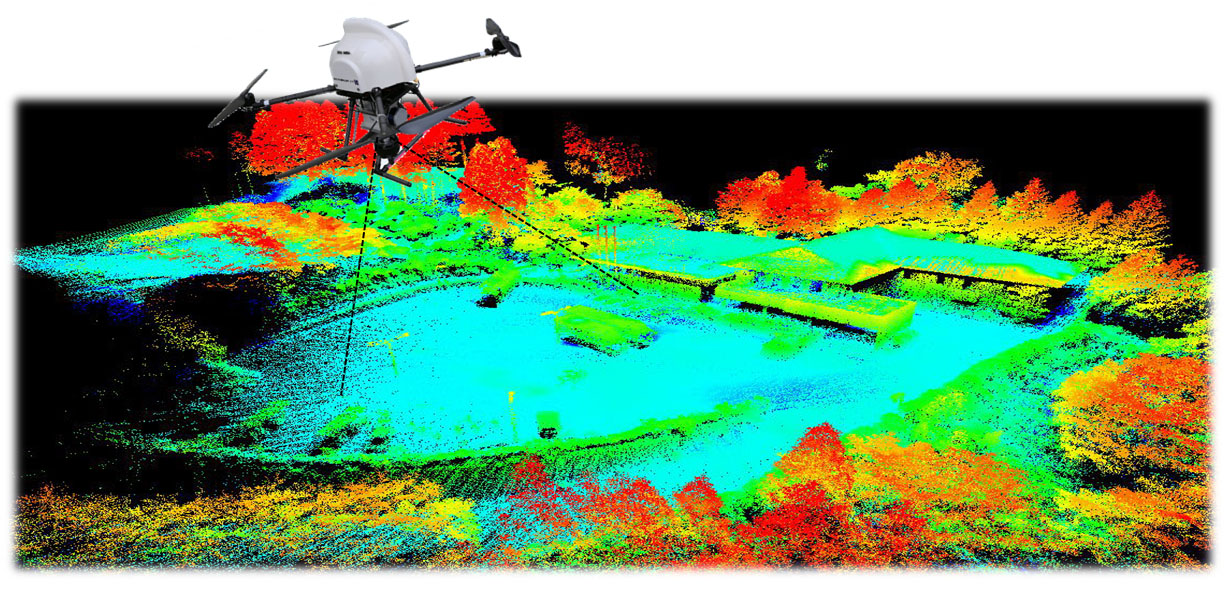
A LIDAR sensor sends out pulses of laser light and measures the exact time it takes for these pulses to return as they bounce from the ground. It also measures the intensity of that reflection. In some specific situations, a terrain model below vegetation is needed as an output. While you can use photogrammetry to effectively create 3D models in areas with sparse vegetation, the higher cost and complexity of LIDAR may be worth it when dealing with areas of relatively dense vegetation. This is because LIDAR light pulses can filter through small openings between the leaves and reach the ground below.
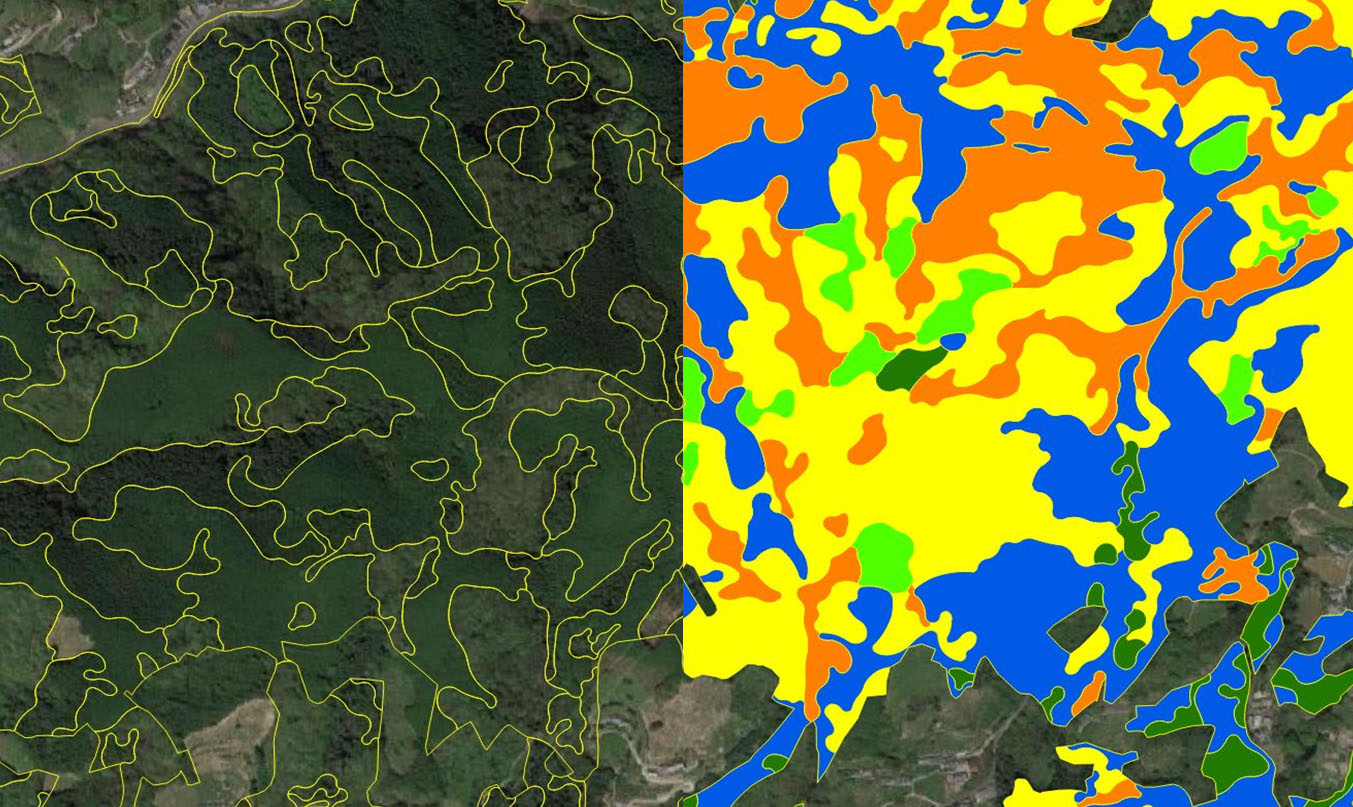
Using aerial photographs and LiDAR data, we have extracted highly accurate tree type classification, forest changes (logging area) and forest roads and counted tree top.
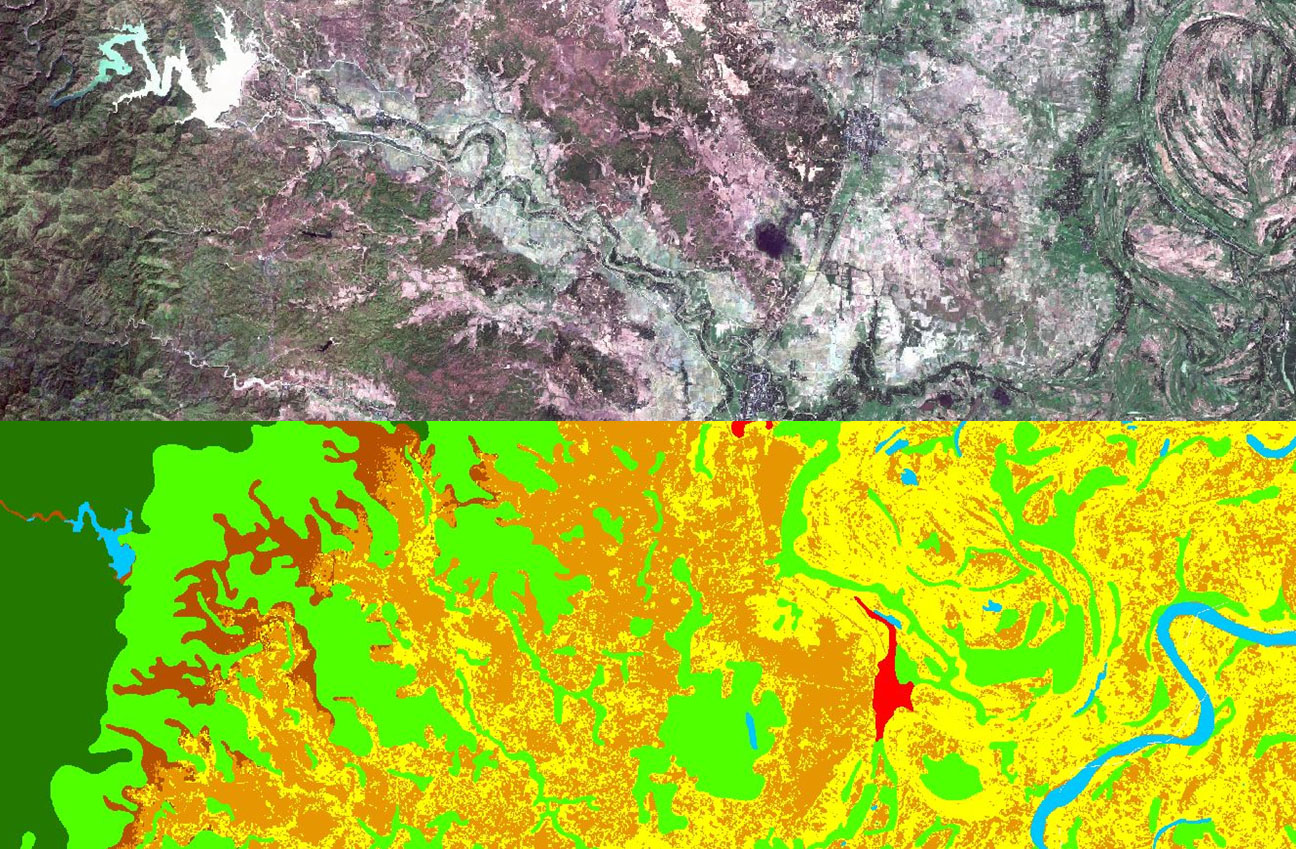
Land cover maps represent spatial information on different types (classes) of physical coverage of the Earth's surface, e.g. forests, croplands, water body, urban area. Dynamic land cover maps include transitions of land cover classes over time and hence captures land cover changes.
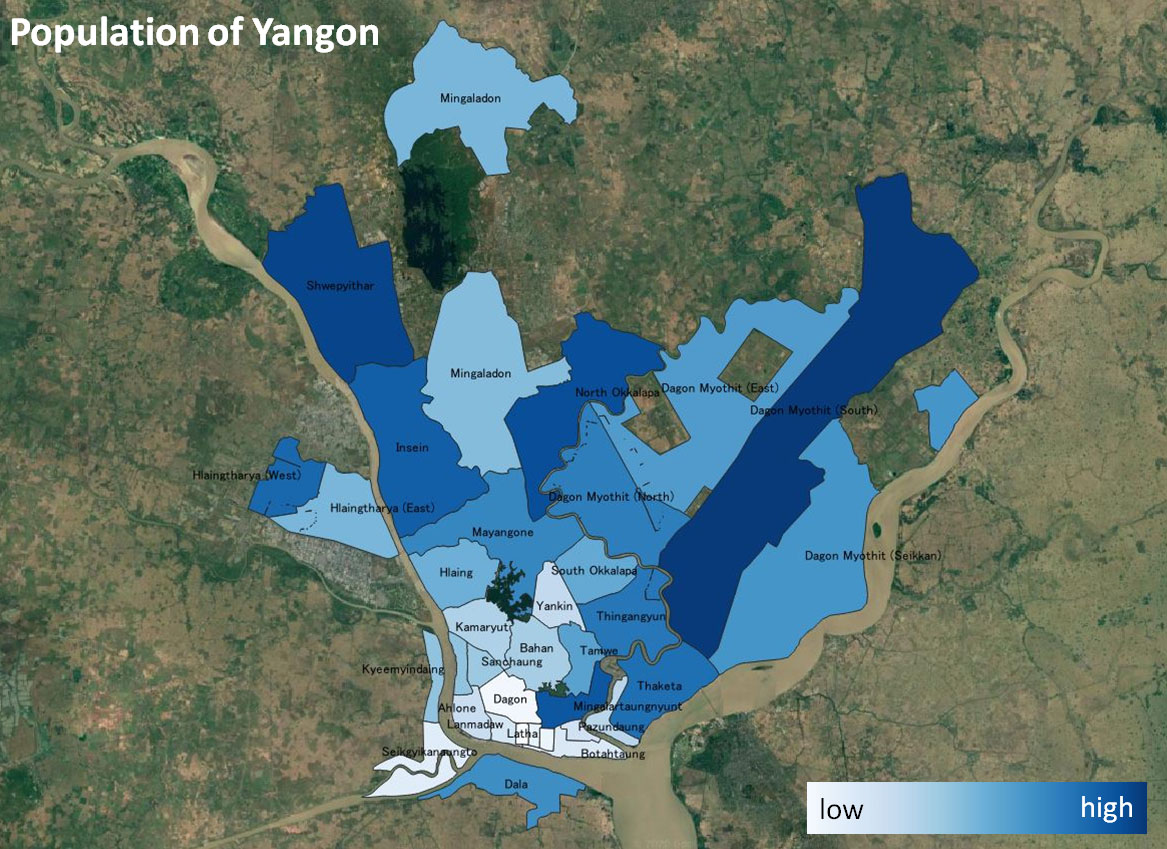
The city of Yangon covers a surface area of 598.75 sq. km. The population density comes to approximately 12,308 individuals living per square kilometer in the urban area of Yangon.